Botulin toxin injections such as Botox® and Dysport® work by temporarily paralysing a portion of the internal sphincter muscle. They do this through a number of mechanisms, including the blockade of the nerves that innervate the smooth muscle of the internal sphincter.
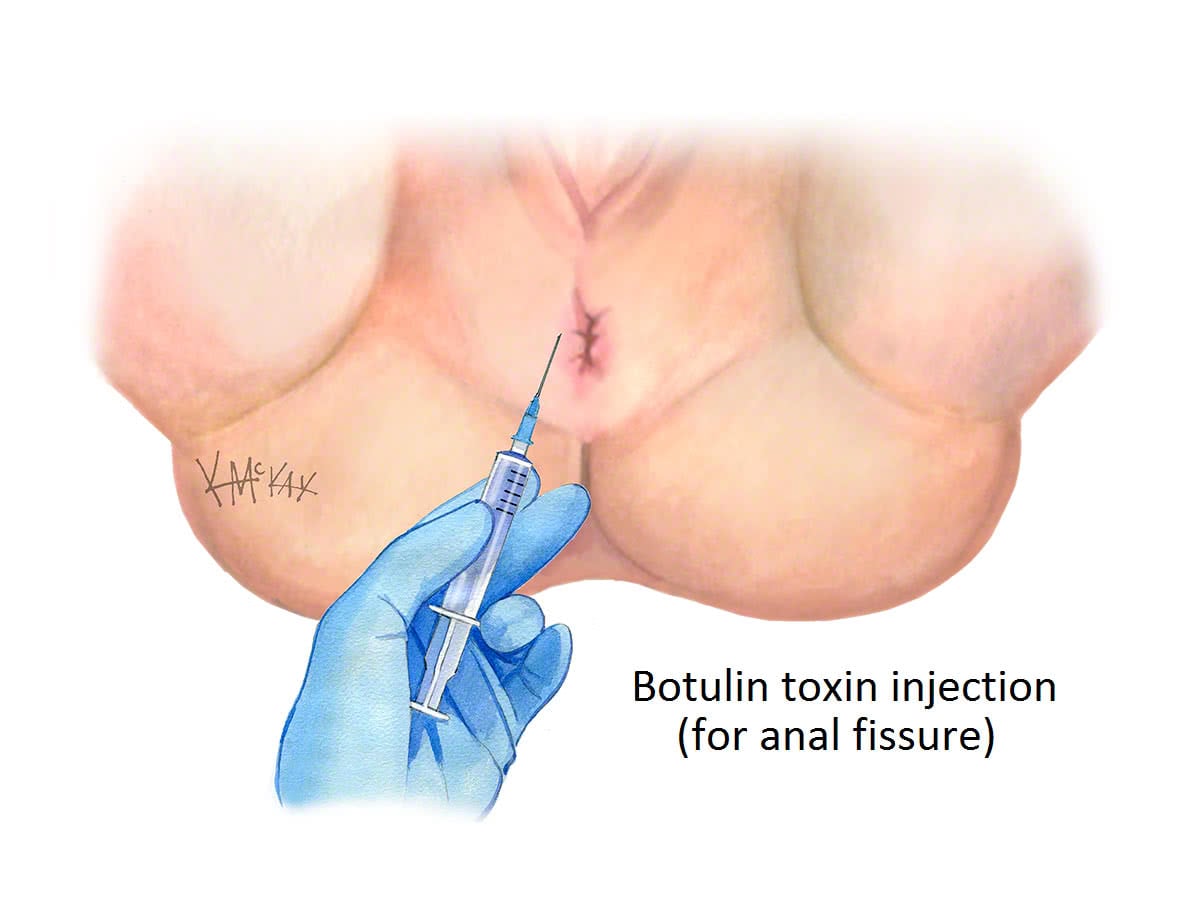
Neurotoxins such as Botultin toxin A have the advantage of being effective in 60-80% of cases as well as being reversible and repeatable. Unfortunately, they are not covered by Medicare or PBS in many public hospitals in Australia, although a number of public hospitals in Sydney have successfully campaigned to make it available free of charge for the treatment of anal fissure. Neurotoxins such as botulin toxin A can be injected in the consulting rooms but the costs of almost $500 per injection remains prohibitive. Neurotoxin injections such as Botulin toxin A for anal fissure administered in a private hospital is usually not covered by your health insurance fund and an out of pocket cost of $500 is usual. On occasions the cost of Botox injection has been approved by some private health insurance companies, on a case-by-case independent appeal mentioning that treatment has failed with topical ointments such a Rectogesic® or 2% diltiazem, and the long-term risk of permanent incontinence associated with surgery (i.e. lateral internal sphincterotomy) is not a reasonable alternative.
There have been reports of temporary incontinence in 20% of patients after botulin toxin A injection [1]. The benefit of Botulin toxin A, is that the paralysing effect only lasts for 2-3 months, with complete recovery of muscle function after this. This is enough time in most cases to allow the anal fissure to heal. Long-term permanent incontinence has not been reported after 1-2 does. This is in contrast to surgery (i.e. lateral internal spincterotomy) where the rates of permanent mild incontinence are as high as 20%, and complete incontinence up to 5%.2 Combination Botulin and topical gels such as those already mentioned are more likely to work than either on its own.
References
-
Nasr M. Ezzat H. Elsebae M. Botulin Toxin Injection versus lateral internal sphincterotomy in the treatment of chronic anal fissure: a randomized controlled trial. World J Surg34:2730-2734 2010 Aug.
